May 30, 2025
The Value of Free Estimates
Why Getting a Professional Quote Matters
When planning any electrical project or repair, knowing the potential costs upfront is crucial. That’s why free estimates are a valuable service offered by professional electricians. Whether you need a panel upgrade, lighting installation, or a full rewiring, a free estimate helps you make informed decisions and ensures transparency in pricing.
Why Free Estimates Matter
- Cost Transparency – A free estimate gives you a clear understanding of the expected expenses before any work begins.
- Informed Decision-Making – Comparing estimates allows you to choose the best service provider for your needs and budget.
- No Financial Obligation – You can explore your options without committing to any upfront costs.
- Accurate Project Planning – Knowing the scope and cost of work helps with budgeting and scheduling.
- Builds Trust with Contractors – A professional who offers a free estimate values transparency and customer satisfaction.
- Project Evaluation – The electrician assesses the work needed and discusses your requirements.
- Cost Breakdown – A detailed list of labor, materials, and any additional expenses.
- Timeframe Estimate – An approximate timeline for project completion.
- Recommendations – Suggestions for the best solutions based on your home or business needs.
- Define Your Needs – Have a clear idea of the work you need done, whether it’s repairs, upgrades, or new installations.
- Ask Questions – Inquire about warranties, permits, and potential challenges related to the project.
- Compare Multiple Estimates – Getting quotes from different professionals ensures you receive fair pricing and quality service.
- Check Credentials – Ensure the electrician is licensed, insured, and has positive customer reviews.
June 26, 2025
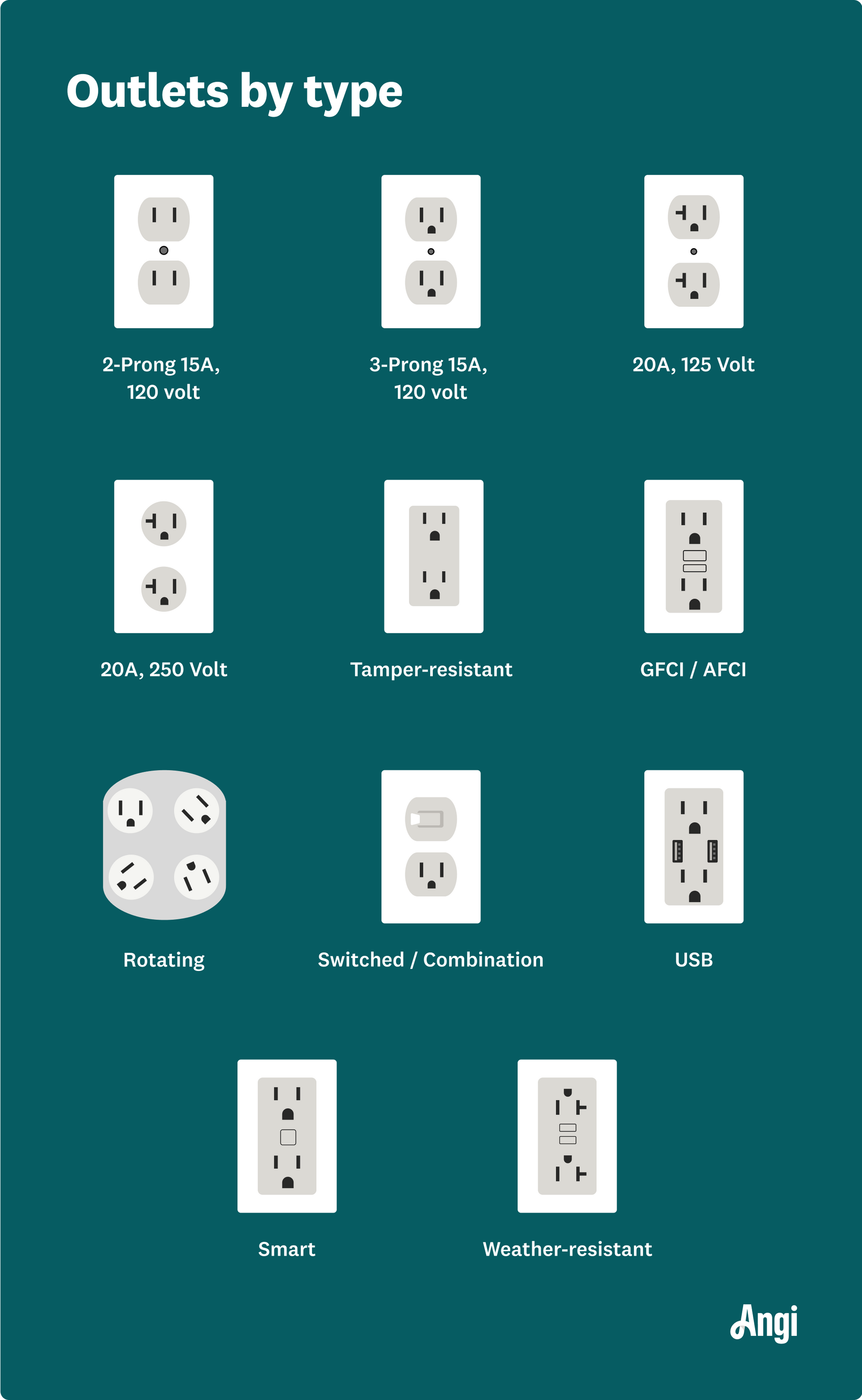
When you plug in an appliance or gadget, one of the most important factors to consider is the voltage that the outlet can support. If the voltage is too high or too low for the device you're using, it can cause malfunctions or even lead to dangerous electrical fires. But how can you easily figure out the voltage that an outlet supports? In this post, we'll walk you through a few methods for determining the voltage of an electrical outlet, and why it's so important to make sure everything is running at the right voltage. 1. Check the Label or Specifications of the Outlet The easiest way to determine the voltage of an outlet is to check the label or specification of your home or office's electrical system. This will typically be displayed on the breaker panel, which is usually located in your basement, utility room, or garage. In most countries, there are standard voltage ratings for home outlets, but there may still be variations based on location or appliance needs. United States: Standard voltage is typically 120V for most outlets (in residential settings), while 240V outlets are used for high-power appliances like dryers and ovens. Europe and most of the world: Most countries use 230V as the standard voltage, but again, there are specific exceptions, so always check your local code. By knowing the standard voltage in your region, you can make a good guess about what an outlet supports. 2. Use a Multimeter to Measure Voltage If you want to be more precise or check a specific outlet, using a digital multimeter is the best way to measure the voltage. Here’s a step-by-step guide: Tools Needed: A digital multimeter Proper safety precautions (i.e., avoid touching metal parts when measuring) Steps: Set your multimeter to measure AC voltage (look for the “V~” symbol on your multimeter). Insert the probes: One probe goes into the “common” (negative) port, and the other goes into the “voltage” (positive) port. Touch the probes to the outlet: Insert the black (negative) probe into the larger slot, and the red (positive) probe into the smaller slot of a typical North American outlet. Read the multimeter: The digital readout will display the voltage of the outlet. For a standard 120V outlet in the U.S., you should see a reading around 110V to 120V. For higher voltage outlets, like those used for large appliances, you might see readings closer to 240V (especially in industrial settings). Safety Tip: If you're not comfortable working with electricity or have doubts about safety, it’s best to call an electrician to do the measurement for you. 3. Look for Specific Outlet Types (Different Voltages for Different Uses) Outlets come in different shapes and sizes, each designed for different voltage requirements. Here’s a quick guide to recognize the type of outlet: Standard 120V Outlet (North America): Two vertical slotted holes, or a round hole along with the two slotted holes (for grounded outlets). 240V Outlet (for high-power devices like electric stoves, dryers, and large air conditioners): Larger, sometimes with three or four holes. They are often round or L-shaped (with varying configurations). European 230V Outlet: Typically a round socket, which usually supports 2-pin or 3-pin plugs depending on the specific region. Check your appliance's plug type and match it with the outlet’s design to confirm if it’s intended for the voltage in your area. 4. Consult with an Electrician If you're unsure about the specifications of your outlet, or if you have concerns about whether it is capable of safely handling a certain voltage, it’s always wise to consult a professional. Electricians can inspect your system, advise on upgrades or repairs, and ensure that everything meets safety standards. Why Voltage Matters Understanding the voltage of an outlet is crucial for several reasons: Device Safety: Plugging a device into an outlet with the wrong voltage can burn out your device’s components, rendering it useless or, worse, causing fires. Energy Efficiency: Using the correct voltage ensures your device runs efficiently and doesn’t consume more power than necessary. Longevity of Appliances: Devices that are exposed to improper voltages may wear out prematurely or operate erratically. By checking the outlet specifications, using a multimeter to test the voltage, or examining the outlet’s design, you can easily figure out what voltage an outlet can support. Whether you’re setting up a new device, troubleshooting an old one, or simply keeping your electrical system safe, understanding voltage is key to maintaining a secure and efficient home or workspace. If in doubt, always consult an electrician to avoid any risks. Better safe than sorry when dealing with electricity!

June 12, 2025
Why Upgrade Your Electrical Panel? 1. Increased Power Capacity – Older electrical panels may not support the energy demands of modern appliances, leading to overloaded circuits and frequent breaker trips. 2. Enhanced Safety – Outdated or faulty panels can pose serious fire hazards due to overheating or arcing. 3. Code Compliance – Electrical codes change over time, and upgrading ensures compliance with current safety standards. 4. Improved Home Value – A new panel can make your home more attractive to buyers and pass home inspections with ease. 5. Support for Home Renovations – If you’re adding a new room, upgrading HVAC systems, or installing a home office, a panel upgrade ensures reliable power distribution. Signs You Need a Service Change or Panel Upgrade • Frequent breaker trips or flickering lights – This could indicate that your panel is struggling to distribute power efficiently. • Fuse box instead of circuit breakers – Older homes may still have fuse boxes, which are outdated and less safe than modern breaker panels. • Burning smell or warm electrical panel – These are warning signs of overheating and potential electrical hazards. • Limited circuits available – If you’re constantly using power strips or extension cords, your panel may not have enough circuits to meet your needs. • Adding high-powered appliances – If you’re installing an EV charger, hot tub, or high-efficiency HVAC system, an upgraded panel may be necessary. The Process of Upgrading Your Electrical Panel 1. Assessment and Planning – A licensed electrician will evaluate your current electrical system and determine the best upgrade solution. 2. Choosing the Right Panel – Options include 100-amp, 150-amp, and 200-amp panels, depending on your home’s power needs. 3. Permitting and Code Compliance – Panel upgrades require permits and must adhere to local electrical codes. 4. Installation and Wiring – The old panel is replaced, new breakers are installed, and wiring is updated as needed. 5. Testing and Final Inspection – The system is tested to ensure safe operation before final approval. Benefits of a Panel Upgrade • Better Energy Efficiency – Reducing strain on your electrical system can lower energy waste and utility costs. • Future-Proofing Your Home – A modern panel allows for future home expansions, EV chargers, or smart home integrations. • Peace of Mind – Knowing your electrical system is safe and up to code provides confidence and security.

May 21, 2025
A Comprehensive Guide to Electric Sauna Wiring: Safety, Codes, and Best Practices Installing an electric sauna in your home offers a luxurious wellness experience, but it also involves meticulous electrical work. Proper wiring ensures safety, efficiency, and longevity of your sauna system. This guide walks you through the essential steps and considerations for wiring an electric sauna, whether you're building a new one or upgrading an existing setup. ________________________________________ Understanding Sauna Electrical Requirements 1. Power Supply & Voltage Most residential saunas operate on a 240V, 60Hz circuit. The required amperage depends on the heater's size: • 6–7 kW heaters: Typically require a 30-amp circuit. • 9 kW heaters: Usually need a 40-amp circuit. • Larger heaters: May demand up to 60 amps. Always consult the manufacturer's specifications to determine the exact requirements. 2. Dedicated Circuit Saunas must be connected to a dedicated circuit, meaning the circuit should supply power exclusively to the sauna. This prevents overloads and ensures the sauna operates safely. 3. Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) Protection GFCI protection is crucial to prevent electrical shocks. Install a GFCI breaker in the main panel or a GFCI disconnect near the sauna to safeguard users. ________________________________________ Wiring Materials and Installation 1. Wiring Type • Indoor Installations: Use NM-B (non-metallic sheathed) cable or conduit where necessary. • Outdoor Installations: Employ weather-rated conduit and junction boxes to protect against environmental factors. 2. Wire Gauge Use appropriately rated wires that can handle the required voltage and current. For example, a 10mm² cable is commonly used for sauna installations. 3. Circuit Protection Ensure the sauna circuit is protected by the correct type and rating of circuit breaker (and RCD, if required by local codes). ________________________________________ Safety Considerations • Avoid Installing Outlets Inside the Sauna: Due to the wet environment, outlets and switches should be installed outside the sauna room to prevent electrical hazards. • Use Heat-Resistant Wiring: Select wiring materials that can withstand high temperatures and humidity levels typically found in saunas. • Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect the wiring and connections for signs of wear or damage to maintain safety and efficiency. ________________________________________ Final Thoughts Proper wiring is essential for the safe and efficient operation of your electric sauna. Always adhere to local electrical codes and consult with a licensed electrician to ensure compliance and safety. By following these guidelines, you can enjoy the benefits of your sauna with peace of mind.

April 29, 2025
As temperatures rise, there’s no better time to upgrade your home or business with a reliable, energy-efficient cooling solution. At Anchor Electric Contracting Corp, we specialize in the professional installation of mini-split systems and traditional air conditioners, providing comfort and peace of mind for our customers throughout the year. Why Choose Anchor Electric for Your Cooling Needs? With decades of experience in residential and commercial electrical contracting, Anchor Electric is your trusted partner for HVAC installation. We bring the same precision, integrity, and attention to detail that we’ve delivered in every project since day one. When you choose us, you get: • Licensed and insured technicians • Clean and efficient installation • Custom solutions tailored to your space • Competitive pricing and clear communication The Benefits of Mini-Split Systems Mini-split systems are a smart alternative to central air—especially for homes without ductwork, or for adding cooling to individual rooms like: • Home offices • Finished basements • Garages • Additions or in-law suites Mini-splits are: • Energy-efficient: Save on utility bills with zone-specific cooling. • Quiet: Enjoy a peaceful environment while staying cool. • Sleek & compact: Modern wall-mounted units blend seamlessly into your space. • Versatile: Heating and cooling capabilities in one system. • Traditional Air Conditioning Done Right Need a central air system installed or upgraded? We’ve got you covered. Anchor Electric handles everything from wiring and power upgrades to unit installation, all to code and with your comfort in mind. Whether you’re building new or replacing an old unit, we make sure your system is sized and installed for optimal performance. Schedule Your Installation Today Don’t wait for the next heat wave to make a change. Anchor Electric Contracting Corp is ready to keep your home or business cool, safe, and energy-efficient. �55357;�56542; Call us today at 406-251-3166 �55357;�56551; Email: customerconnect@anchorlt.com �55356;�57104; Visit: www.anchorelectricmt.com






